General Introduction
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) defines a payment system as a set of instruments, procedures, and rules for the transfer of funds between or among participants; and the system includes the participants and the entity operating the arrangement.
The principal objective of the payment system is to enhance the stability of the financial system, reduce transaction costs in the economy, promote the efficient use of financial resources, and improve financial market liquidity. Thus, the payment system is not only a key component of the financial market infrastructure, but also a key channel for the conduct of monetary policy.
With the emergence of new technology, a number of innovative non-cash payment instruments have been brought into use to meet consumers’ payment needs, leading to the introduction of new payment systems that enable faster and more efficient payment and settlement processing. The smooth operation of these systems allows individuals, enterprises, and organizations to fulfill their financial obligations and transfer funds safely and in a timely manner.
In line with international trends and development of the payment system, the responsibility of the central banks to ensure the stability, reliability and efficiency of the payment system has significantly increased around the world.
Within the framework of reforming the legal environment of the payment system of Mongolia, the Law on National Payment System was approved on May 31, 2017 and became effective on January 1, 2018. The law establishes the legal and organizational framework for the national payment system; governs the procedure for providing payment services and the activities of the participants of the national payment system; defines the organizational and operating requirements for payment service providers and operators; and sets procedures for exercising supervision and oversight with respect to the national payment system. This law also allows non-bank entities to participate in the national payment system.
The role of the Central Bank of Mongolia in the national payment system
The Bank of Mongolia plays a crucial role in the national payment system and thrives to maintain the safe, efficient, and smooth operation of the national payment system that meets the needs of the national economy and society.
According to Article 6 of the Law on National Payment System, "The Bank of Mongolia shall manage, regulate and oversee the national payment system and its activities"; thus, the Bank of Mongolia conducts the following activities:
- Define national payment system policy;
- Issue relevant licenses to the system’s participants who fully meet the criteria;
- Approve rules and regulations related to the oversight of the national payment system and its operation; issuance of payment instruments; and provision of payment services;
- Monitor the activities of the licensee in the payment system;
- Perform other prescribed activities related to payment, clearing and settlement system and the issuance of payment instruments.
In order to ensure the secure operation of the payment system and protect the consumers, the Bank of Mongolia assesses the new payment instruments and services, issues relevant licenses to system participants who fully meets the criteria, and if required, may carry out annual inspections to check compliance of banks and other payment service providers participating in the payment system.
General structure
The payment system of Mongolia consists of three subsystems (Figure 1): Real Time Gross Settlement system (RTGS) for large-value payments, Automated Clearing House system (ACH +) for low-value payments, and the interbank payment card system.
Real time gross settlement (RTGS) system for large-value transactions enables participants to transfer funds over MNT 3 million per transaction, the amount approved by the resolution of the Governor of the Bank of Mongolia. The system also allows participants to obtain intraday liquidity; therefore, reducing settlement risk, perform the interbank settlement process on the real time basis, monitor liquidity, balance account and settlement stream on the actual time basis.
The Automated Clearing House (ACH +) system transfers low-value payments, amounting to MNT 3 million or less per transactions. The system also allows participants to send and receive transactions either in real time and continuously for 24/7 or through batch payments that are sent and received within a certain interval of time. The transactions are then cleared on a net basis in the ACH + system and the final settlement takes place in the RTGS system within the same working day or the next day depending on the settlement session the transaction falls in.
Interbank card transactions are also processed through the National Electronic Transaction Center (NETC) of the Bank of Mongolia infrastructure, and the payments between participants are cleared on a net basis, whereas the final settlement takes place in the RTGS system on the following business day and the results are then reflected in the accounts held at the central bank of the system participants.
The National Electronic Transaction Center (NETC) of the Bank of Mongolia is responsible for the clearing of card transactions of direct participants, while the Trade and Development Bank is responsible for clearing of card transactions of indirect participants.
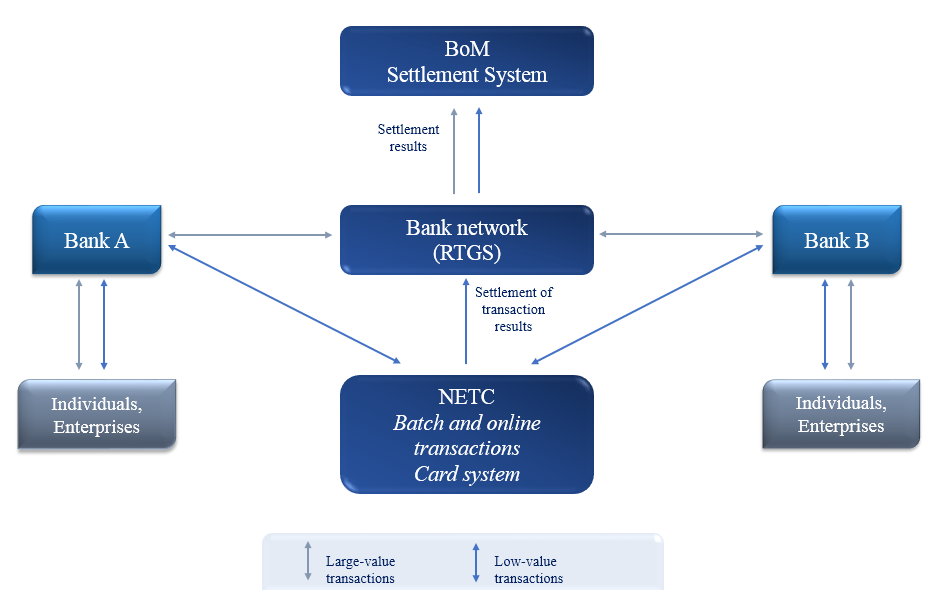
Figure 1. Interbank transaction systems
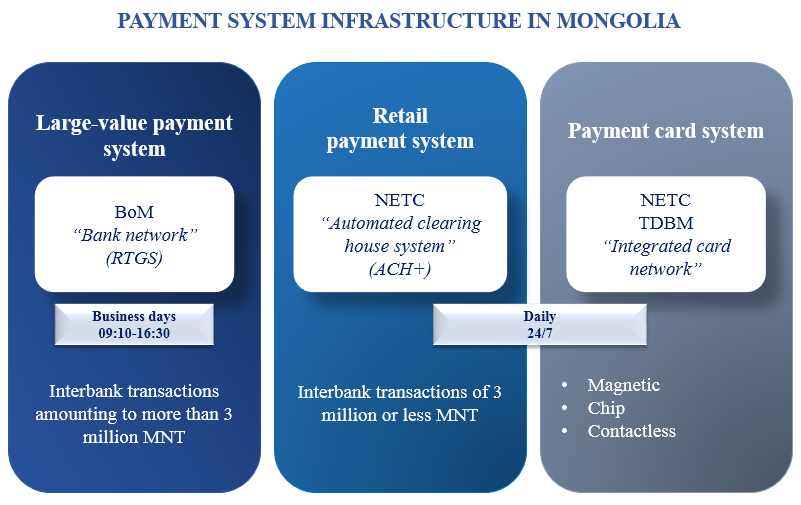
Figure 2. Diagram of the large and low value interbank transaction system
The number of new payment instruments and services entering the market is increasing year by year as a result of the Bank of Mongolia's strategy to ensure safe, reliable, and efficient operation of payment systems, support the use of non-cash payments, and develop the financial market infrastructure.
With the introduction of the Law on the National Payment System, competition in the payment system arena has intensified as non-bank financial institutions and other payment service providers are competing directly with banks by successfully introducing new payment products and services into the market using latest technology.
Payment instruments and channels used in Mongolia:
- Cash
- Internet bank
- Payment orders and invoices
- Mobile bank
- Payment cards
- Remittances
- E-money
- Billing
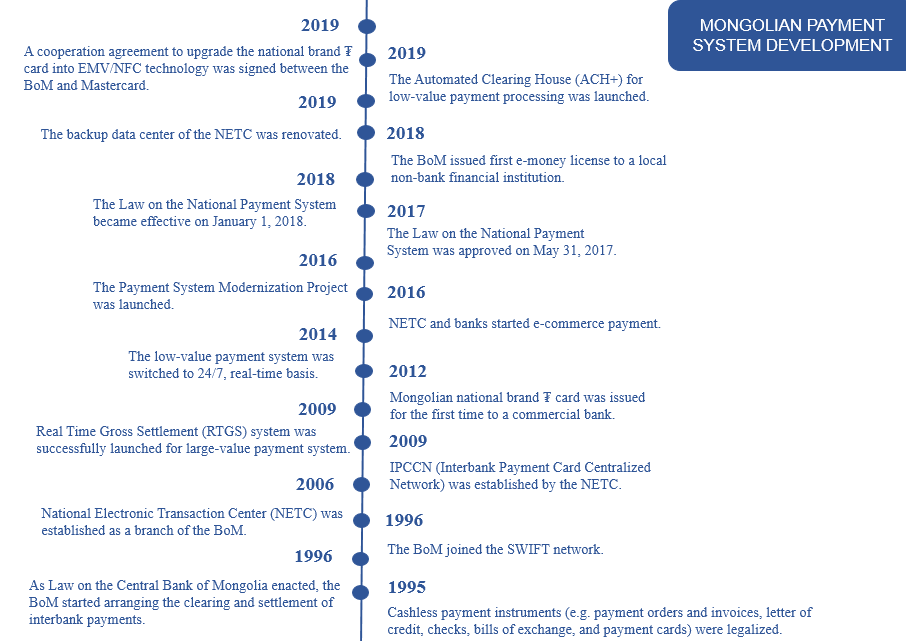
Figure 3. Timeline of development of payment system in Mongolia